Innovation in Food Processing with MATS & MAPS Technology
Contents
In the rapidly evolving food industry, MATS (Microwave Assisted Thermal Sterilization) and MAPS (Microwave Assisted Pasteurization System) stand out as game-changing solutions. These cutting-edge technologies offer efficient methods for sterilizing and pasteurizing food products, ensuring enhanced safety and nutritional value.
MATS and MAPS represent a paradigm shift in the food processing industry. MATS uses microwave energy to rapidly and uniformly heat food products, eliminating harmful pathogens while preserving taste, texture, and nutrients. MAPS, on the other hand, utilizes microwave technology for pasteurization, achieving similar pathogen reduction while retaining the freshness and nutritional value of perishable foods. Titan Engineering and Automation Limited (TEAL), a leader in this industry, has embraced these technologies to design and build state-of-the-art production lines.
TEAL's forward-thinking approach and commitment to innovation have led to the adoption of MATS and MAPS technologies. By integrating these technologies seamlessly into existing food processing operations, we aim to empower manufacturers to revolutionize their production processes while meeting stringent quality and safety standards.
Harnessing the Power of Microwaves: An Introduction to MATS and MAPS in Food Processing
MATS and MAPS are sophisticated, microwave-based thermal processing technologies utilized for food sterilization and pasteurization. Dr. Juming Tang, Distinguished Chair of Food Engineering at Washington State University, is the visionary behind the groundbreaking MATS technology. His innovative research in Microwave Assisted Thermal Sterilization has revolutionized food processing, ensuring enhanced safety and nutritional value while extending shelf life. Dr. Tang's expertise has left an indelible mark on the industry, inspiring advancements in food engineering for a safer and more nutritious future.
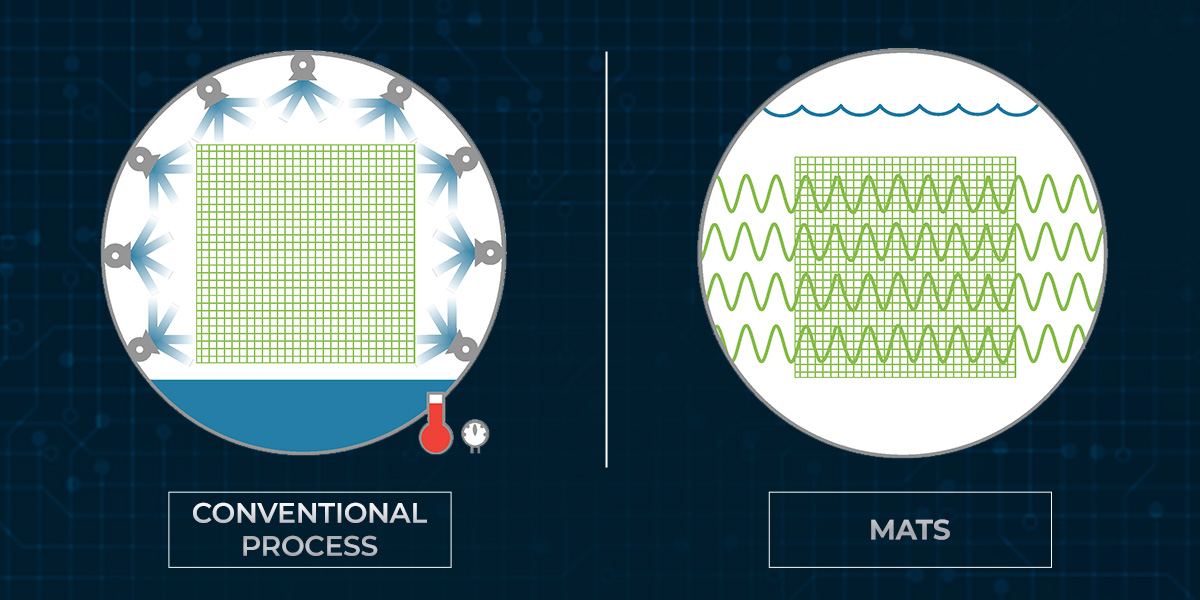
In conventional processing methods, packaged food is subjected to high temperatures for extended periods. Unfortunately, this prolonged exposure to high temperatures leads to a significant loss of nutrients and adversely affects the taste and texture of the foods. To counterbalance this deterioration, food manufacturers resort to adding excessive salt and artificial additives to enhance flavor, texture, and appearance. However, the revolutionary MATS process offers a transformative alternative to conventional food processing.
With MATS, the approach to food processing undergoes a remarkable shift. The technology submerges packaged food in hot water (pressurized vessel) while simultaneously subjecting it to microwave energy. This innovative combination swiftly eliminates harmful pathogens and spoilage microorganisms in just a matter of minutes. Notably, this patented process preserves the vital nutrients, natural color, appealing texture, and delectable flavor of foods, while remarkably extending their shelf life to a level equivalent to conventionally processed foods. By embracing MATS, the food industry revolutionizes the way food is processed, ensuring greater nutritional retention and offering consumers a safer and more enjoyable culinary experience.
What are the benefits of MATS and MAPS technology?
The adoption of MATS and MAPS technologies in the food industry offers a multitude of benefits compared to traditional thermal processing methods. These innovative technologies revolutionize food processing and bring significant advantages to both manufacturers and consumers. Here are some key benefits of MATS and MAPS technology:
- Enhanced Product Quality: The precise and uniform heat distribution in MATS and MAPS systems preserves the nutritional content, taste, texture, and color of the food. This results in food products that maintain their original quality, offering consumers an exceptional sensory experience.
- Extended Shelf Life: MATS and MAPS technologies carefully and efficiently process food, extending its shelf life compared to traditional methods. By controlling the thermal processing parameters, these technologies maintain the freshness and quality of food products for an extended period. This provides consumers with a wider range of convenient, nutritious, and long-lasting ready-to-eat options.
- Sustainable Food Processing: By utilizing MATS and MAPS technologies, manufacturers can promote sustainability in the food industry. These technologies contribute to reducing food waste through extended shelf life, minimizing the need for artificial additives, and optimizing energy usage, thereby supporting environmentally friendly practices.
As the food industry continues to evolve, MATS and MAPS technologies play a pivotal role in shaping the future of safe, nutritious, and flavorful ready-to-eat food products.
Exploring the Applications of MATS and MAPS
MATS and MAPS technologies have a wide range of applications in the food industry. These innovative processing methods offer numerous benefits and are suitable for various food products. Here are some applications of MATS and MAPS:
- Ready-to-Eat Meals: MATS and MAPS technologies are ideal for processing ready-to-eat meals, such as pre-packaged entrees, soups, stews, and side dishes. These technologies ensure that meals are thoroughly sterilized or pasteurized while preserving their quality and taste.
- Sauces and Condiments: MATS and MAPS can be used to process sauces, dressings, and condiments, ensuring that they are safe for consumption and maintaining their flavor and texture. This enables manufacturers to produce shelf-stable products without the need for excessive preservatives.
- Baby Food: MATS and MAPS are suitable for processing baby food, ensuring that it is free from harmful pathogens and bacteria. The technologies preserve the nutritional value of the food while extending its shelf life, providing convenience for parents and caregivers.
- Beverages: MAPS technology is particularly beneficial for pasteurizing beverages, such as juices, dairy-based drinks, and ready-to-drink coffee and tea. It eliminates viral and bacterial pathogens, extending the shelf life of these beverages while maintaining their taste and quality.
- Food Service and Industrial Applications: MATS and MAPS technologies find applications in food service and industrial settings, providing a safe and efficient method for processing large quantities of food products. These technologies enable manufacturers to meet the demands of the food service industry while ensuring food safety and quality.
MATS and MAPS applications in the food industry are expanding. TEAL is spearheading this change. Let us see how we are contributing to the advancements of this industry.
How TEAL is paving the Way in the Food Industry with MATS Technology
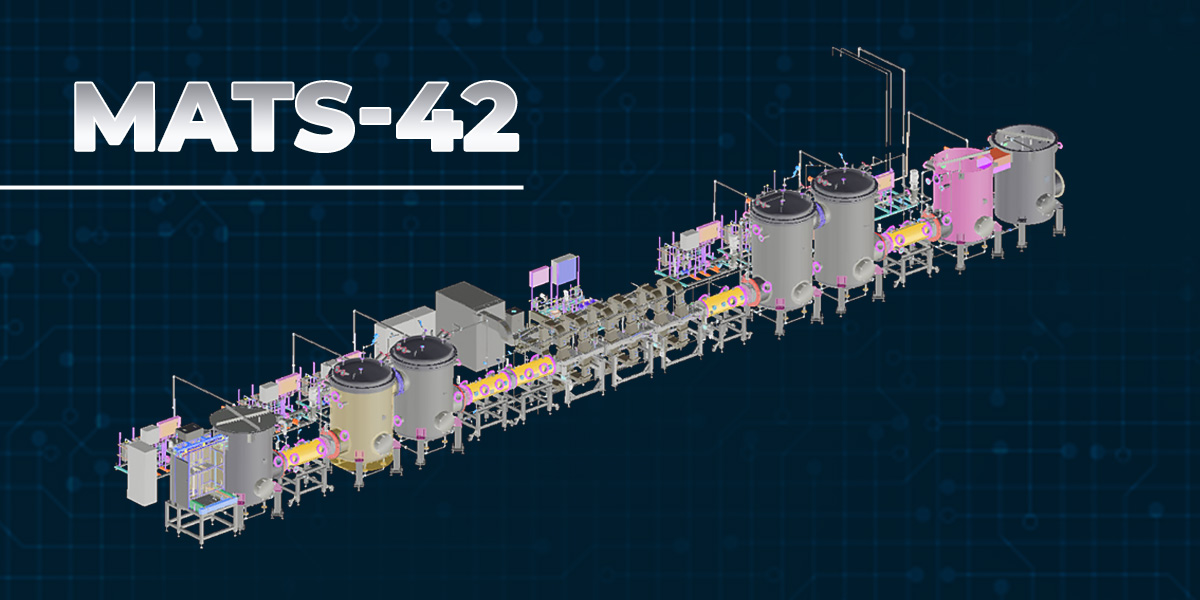
TEAL is at the forefront of revolutionizing the food industry with its top-notch adoption of MATS and MAPS technologies. As a leader in providing automation solutions and production lines, our expertise in designing and implementing state-of-the-art MATS machines for food sterilization, sets a new standard for food processing operations.
TEAL customized solutions cater to specific client requirements and industry standards. By collaborating closely with client and comprehending their goals, we ensure that the MATS machines seamlessly integrate into existing operations, optimizing efficiency and product quality.
Frequently Asked Questions
Microwaves are utilized in food preservation through two main processes: Microwave Assisted Thermal Sterilization (MATS) and Microwave Assisted Pasteurization System (MAPS).
● MATS is a revolutionary food preservation technology that combines microwave energy and pressurized hot water to sterilize packaged food products rapidly and uniformly. In this process, packaged food is immersed in pressurized hot water and heated with microwave energy at a specific frequency, typically 915 MHz. The combination of high temperature and microwave energy effectively eliminates harmful pathogens and spoilage microorganisms in a matter of minutes. The quick and precise sterilization process ensures that the food's nutrients, color, texture, and flavor are preserved, resulting in high-quality, ready-to-eat products.
● MAPS is a related technology that employs microwaves for pasteurizing foods and beverages. Like MATS, MAPS utilizes microwave energy at 915 megahertz to heat food products to a temperature of 70-90°C for a short duration, usually up to 10 minutes. The process effectively eliminates viral and bacterial pathogens while preserving the sensory attributes and nutritional content of the food. MAPS-processed foods and beverages offer a restaurant-quality taste and texture and have a shelf life of up to 12 weeks.
Microwave sterilization is a process that utilizes microwave energy to eliminate harmful microorganisms, such as bacteria, viruses, and moulds, from food products and other materials. The process involves subjecting the items to high-frequency electromagnetic waves, typically at a frequency of 915 MHz, which causes water molecules in the material to vibrate and generate heat. This rapid and uniform heating effectively raises the temperature of the material, leading to thermal sterilization.
During microwave sterilization, the high temperatures achieved in a short time period result in the destruction of microorganisms, ensuring that the treated items are safe for consumption or use. The process is commonly used in the food industry to preserve packaged food products, as well as in medical and pharmaceutical applications for sterilizing medical instruments and equipment.
Overall, microwave sterilization is a valuable technology that plays a crucial role in enhancing food safety and preserving the quality of various materials in a rapid, efficient, and effective manner.
Autoclaves and microwaves are both used for sterilization, but they differ in their methods and applications. Autoclaves utilize high-pressure steam to sterilize objects by subjecting them to elevated temperatures for a specific duration. This method is commonly employed in medical and laboratory settings to sterilize instruments, glassware, and equipment. On the other hand, microwaves use electromagnetic waves to rapidly heat the material being sterilized. This efficient method is widely used in the food industry for sterilizing packaged foods and beverages, as well as in some medical and pharmaceutical applications.
One of the main distinctions lies in the processing time. Autoclaves generally require longer sterilization cycles due to the heating and cooling phases, while microwaves offer quick and effective sterilization with reduced processing time. Additionally, autoclaves are versatile and suitable for various materials, including glass, metal, and some plastics, ensuring steam penetration into porous and hard-to-reach areas. Microwaves, however, may have limitations in penetrating certain materials with low microwave absorptivity.
The choice between an autoclave and a microwave depends on the specific application, material compatibility, and desired speed of sterilization. Autoclaves excel in medical and laboratory environments, while microwaves are particularly efficient for the food industry and selected medical and pharmaceutical uses.
The principle of microwave-assisted techniques is based on the ability of microwaves to interact with polar molecules, such as water, in a substance. When microwaves are applied to a material, the electromagnetic waves cause the polar molecules to rapidly oscillate and generate heat. This localized and rapid heating leads to a quick increase in temperature within the material.
In the context of food processing and sterilization, microwave-assisted techniques are utilized to heat the food products rapidly and uniformly. For instance, in Microwave Assisted Thermal Sterilization (MATS) and Microwave Assisted Pasteurization System (MAPS), packaged food is subjected to pressurized hot water while simultaneously exposed to microwave energy. This combination of heat and microwave energy ensures that the food is rapidly heated, effectively eliminating harmful pathogens and spoilage microorganisms in a matter of minutes.
The principle of microwave-assisted techniques offers several advantages, including faster processing times, reduced energy consumption, and the preservation of the nutritional quality and sensory attributes of food products. By harnessing the power of microwaves for precise and efficient heating, these techniques have revolutionized the food industry by providing safe, nutritious, and flavorful ready-to-eat products with extended shelf life.
